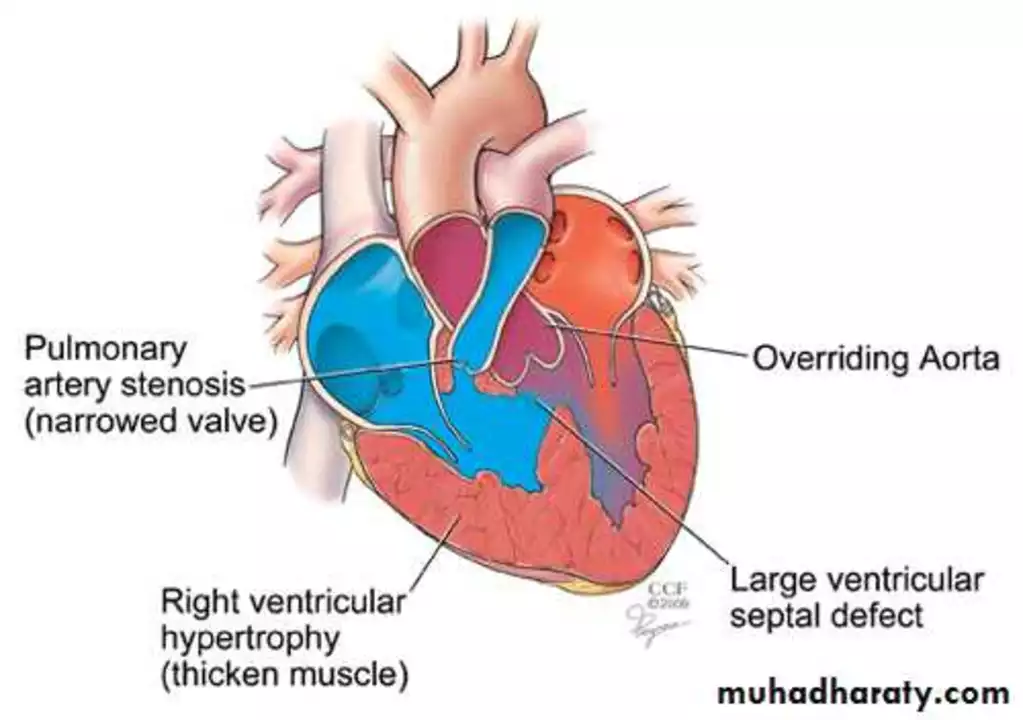
Understanding Left Ventricular Failure
Before diving into the connection between alcohol consumption and left ventricular failure, it is essential to understand what left ventricular failure is. Left ventricular failure, also known as congestive heart failure or simply heart failure, occurs when the left ventricle of the heart is unable to pump blood effectively. This can lead to a buildup of fluid in the lungs and other parts of the body, causing shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and ankles.
As a blogger who is passionate about health and wellness, I feel it's important to raise awareness about the potential risks associated with alcohol consumption, particularly when it comes to heart health. In this article, we will explore the link between alcohol and left ventricular failure, and discuss how you can protect yourself and your loved ones.
Alcohol: A Risk Factor for Heart Failure?
Research has shown that excessive alcohol consumption can be a risk factor for developing left ventricular failure. It is well-established that long-term, heavy alcohol use can lead to a condition called alcoholic cardiomyopathy, which weakens the heart muscle and reduces its ability to pump blood effectively. This condition is a direct result of the toxic effects of alcohol on the heart muscle cells, and can eventually lead to left ventricular failure.
Moderate alcohol consumption, on the other hand, has been shown to have some potential heart health benefits, particularly when it comes to red wine. However, it is important to remember that these benefits are not guaranteed, and the risks associated with heavy drinking far outweigh any potential advantages.
How Much is Too Much?
When it comes to alcohol consumption, the key is moderation. But what constitutes "moderate" drinking? According to the American Heart Association, moderate alcohol consumption is defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
It is important to note that this definition is based on the average daily consumption, and does not mean that you can save up your drinks for the weekend and binge without consequences. Binge drinking can still increase your risk of developing left ventricular failure and other heart-related problems, even if your overall alcohol consumption falls within the "moderate" range.
Beyond Alcohol: Other Risk Factors for Left Ventricular Failure
While alcohol consumption can play a role in the development of left ventricular failure, it is just one of many potential risk factors. Other factors that can contribute to the development of heart failure include high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, diabetes, obesity, and smoking. It's important to remember that reducing your alcohol intake is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to protecting your heart health.
By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress reduction techniques, you can significantly lower your risk of developing left ventricular failure and other cardiovascular issues.
Recognizing the Warning Signs
Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing left ventricular failure and preventing its progression. If you or a loved one has a history of heavy alcohol use, it's essential to be vigilant about monitoring for symptoms of heart failure. These may include shortness of breath, persistent coughing or wheezing, fatigue, swelling in the legs and ankles, rapid weight gain, and irregular heartbeat.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Supporting Recovery and Maintaining Heart Health
If you or a loved one is struggling with alcohol addiction and concerned about the potential impact on heart health, seeking help from a professional is crucial. Recovery from alcohol addiction often involves a combination of medical detox, counseling, and support groups, which can help individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms and reduce their risk of relapse.
In addition to addressing alcohol addiction, it's essential to adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle and work closely with healthcare providers to manage any existing risk factors for left ventricular failure. By taking a proactive approach to both addiction recovery and heart health, you can significantly improve your overall well-being and reduce your risk of developing left ventricular failure.

The relationship between booze and the left ventricle is far more intricate than a quick headline suggests. Chronic overindulgence drenches cardiac muscle cells in a toxic cocktail, eroding their contractile vigor. This stealthy erosion, known as alcoholic cardiomyopathy, can silently reshape the heart's architecture. When the left ventricle loses its punch, blood backs up into the pulmonary circuit, spawning the classic breathlessness that many dismiss as “just tired”. Even a seemingly modest nightly glass can tip the scales if paired with hypertension or genetic predisposition. Studies from the American Heart Association reveal a dose‑response curve where risk escalates sharply after two drinks per day for men and one for women. The metabolic by‑products of ethanol, such as acetaldehyde, wreak havoc on mitochondrial function, starving heart cells of the energy they desperately need. Moreover, ethanol‑induced oxidative stress fuels fibrotic tissue, further stiffening the ventricle and sabotaging its ability to fill and eject blood efficiently. While red wine enthusiasts tout resveratrol as a savior, the net benefit evaporates once consumption breaches moderate limits. Clinicians frequently observe that patients who cut back from binge patterns experience measurable improvements in ejection fraction within months. Therefore, moderation isn’t merely a polite suggestion-it’s a physiological imperative. If you have a family history of heart failure, treat each drink as a potential catalyst, not a harmless toast. Lifestyle interventions-regular aerobic activity, a Mediterranean‑style diet, and diligent blood pressure control-serve as a protective armor around the heart. Should you notice swelling in the ankles, persistent fatigue, or unexplained weight gain, seek a cardiac evaluation promptly. Early detection can halt progression and open the door to therapies that reverse remodeling. In short, the safest route to a resilient left ventricle is to keep alcohol consumption well within the modest bounds prescribed by evidence‑based guidelines.
A single drink a day can still add up over years.
From a hemodynamic perspective, ethanol exerts negative inotropic effects that diminish stroke volume. The resulting increase in end‑diastolic pressure predisposes the myocardium to dilatation. Epidemiological data consistently demonstrate a J‑shaped curve correlating intake with incidence of systolic dysfunction. It is crucial to differentiate between acute intoxication, which transiently depresses contractility, and chronic consumption, which leads to irreversible structural remodeling.
i get what you r saying, but sometimes life throws u into a brawl with stress n alcohol. we all need a lil escape, ya know? yet, the heart’s kinda like a fragile vase – one too many knocks and it cracks. maybe finding a chill hobby or a quiet walk can keep the mind off the bottle. stay easy, stay alive.
It is advisable to approach the topic of alcohol consumption with measured decorum, acknowledging both the epidemiological evidence and individual variability. The physician’s role includes elucidating the nuanced risk profile for patients with pre‑existing cardiac conditions. In doing so, one must balance clinical guidance with respect for patient autonomy. Ultimately, an evidence‑based recommendation remains the cornerstone of prudent medical practice.
Indeed, a collaborative approach can empower patients to make healthier choices. By setting realistic, incremental goals for reducing intake, individuals often experience a surge in confidence and overall wellbeing. Let us encourage one another to prioritize heart health while fostering a supportive community.
Behind the glossy public health campaigns lies a hidden agenda: the alcohol industry subtly manipulates data to downplay the heart risks, while secret societies profit from our dependence. It’s not just about personal choice; it’s a coordinated effort to keep us complacent, ensuring they maintain control over our bodies and minds.
The claim that clandestine entities influence medical guidelines lacks empirical corroboration. Peer‑reviewed literature consistently attributes cardiovascular outcomes to measurable physiological mechanisms, not conspiratorial interference. Maintaining a rigorous, evidence‑based stance is essential for sound clinical reasoning.
I understand how overwhelming this information can feel, especially when personal experiences are involved. It’s important to remember that making incremental changes-whether cutting back on drinks or adding a short walk-can lead to meaningful improvements in heart health. Let’s support each other in navigating these choices with compassion and patience.