Introduction to Atenolol-Chlorthalidone
Atenolol-Chlorthalidone is a combination medication that is commonly prescribed to treat high blood pressure. Atenolol is a beta-blocker, which works by reducing the workload on the heart and helping it to beat more regularly. Chlorthalidone is a diuretic, which helps the body to get rid of excess fluid and salt, thereby lowering blood pressure. In this article, we will explore the impact of Atenolol-Chlorthalidone on immune system function.
The Importance of Immune System Function
The immune system is our body's defense mechanism against harmful substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and toxins. It plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. A strong and properly functioning immune system can help prevent infections and other diseases, whereas a compromised immune system can leave us vulnerable to various health issues. Therefore, it is crucial to understand how medications like Atenolol-Chlorthalidone may affect our immune system and overall health.
Atenolol-Chlorthalidone and the Innate Immune System
The innate immune system is our body's first line of defense against pathogens. It includes physical barriers like the skin, as well as cells such as macrophages and neutrophils that help to eliminate harmful substances. Research has shown that beta-blockers, like Atenolol, may have immunomodulatory effects on the innate immune system. Some studies have found that beta-blockers can reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increase the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, leading to a decrease in overall inflammation. However, more research is needed to fully understand the impact of Atenolol-Chlorthalidone on the innate immune system.
Effects of Atenolol-Chlorthalidone on the Adaptive Immune System
The adaptive immune system is our body's second line of defense and is responsible for creating a specific response to pathogens. It involves the activation of T cells and B cells, which produce antibodies to help neutralize harmful substances. Some studies have suggested that beta-blockers may suppress the function of T cells and B cells, potentially leading to a weakened adaptive immune response. However, further research is needed to determine the exact effects of Atenolol-Chlorthalidone on the adaptive immune system.
Impact on Inflammation and Immune System Function
Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation can contribute to various health issues, including heart disease and autoimmune disorders. As mentioned earlier, beta-blockers like Atenolol have been shown to modulate inflammation by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increasing the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines. This may have potential benefits for immune system function and overall health, but more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Atenolol-Chlorthalidone and Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, leading to inflammation and damage. Some research has suggested that beta-blockers may have potential benefits in treating certain autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis. This is due to their immunomodulatory effects and potential to reduce inflammation. However, more research is needed to determine the efficacy of Atenolol-Chlorthalidone in treating autoimmune disorders and its overall impact on immune system function.
Side Effects and Drug Interactions
As with any medication, Atenolol-Chlorthalidone may cause side effects and interact with other medications. Common side effects may include dizziness, lightheadedness, and fatigue. It is important to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider and inform them of any other medications you are currently taking. This will help to minimize the risk of drug interactions and ensure that Atenolol-Chlorthalidone is safe and effective for you.
Monitoring Immune System Function While Taking Atenolol-Chlorthalidone
If you are prescribed Atenolol-Chlorthalidone, it is important to monitor your immune system function and overall health. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help to identify any changes in your immune system and address any potential concerns. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and engaging in activities that support immune system function, such as exercise and proper nutrition, can further help to ensure your overall well-being.
Conclusion
Atenolol-Chlorthalidone is a combination medication commonly prescribed to treat high blood pressure. While some research has suggested that it may have immunomodulatory effects and potential benefits for immune system function, more research is needed to fully understand its impact. If you are prescribed Atenolol-Chlorthalidone, it is important to monitor your immune system function and overall health, and to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
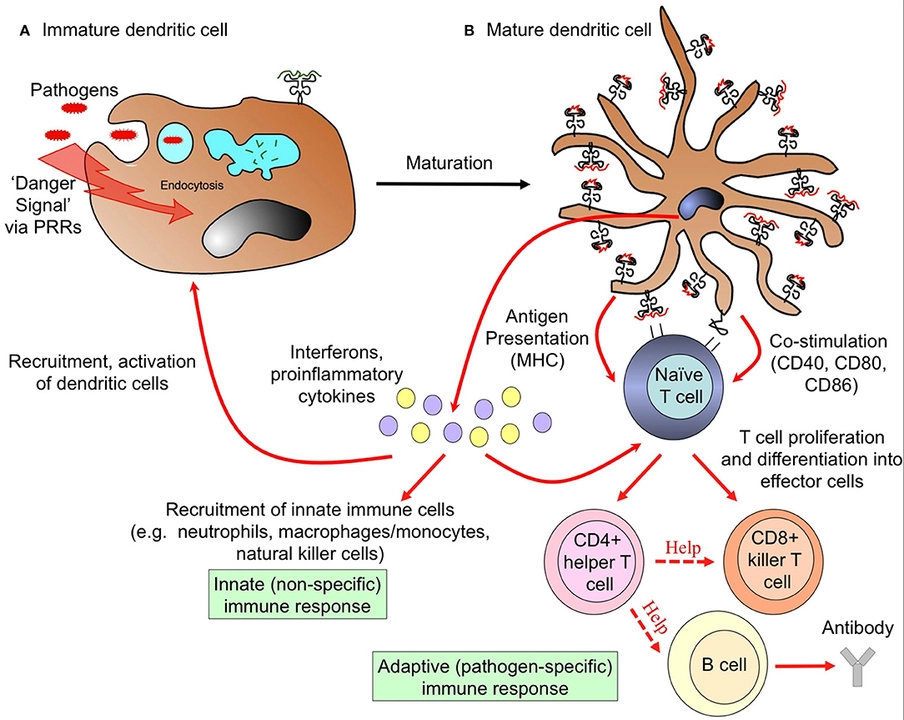
From a mechanistic standpoint, the β‑adrenergic blockade introduced by atenolol can attenuate sympathetic overdrive, which in turn modulates the NF‑κB signaling cascade; this downstream effect often translates to a measurable reduction in pro‑inflammatory cytokine output such as IL‑6 and TNF‑α. Additionally, chlormadinone’s thiazide‑like diuretic action facilitates natriuresis, indirectly influencing endothelial shear stress and thereby fine‑tuning innate immune cell trafficking. When these two pharmacodynamic axes intersect, clinicians observe a nuanced immunomodulatory profile that hinges on dose‑response relationships and patient‑specific pharmacogenomics. In practice, the synergistic attenuation of both hemodynamic load and neuro‑humoral activation may foster a milieu conducive to immune homeostasis, especially in hypertensive cohorts with concurrent metabolic syndrome.
Picture this: a heart that no longer drums like a frantic drummer, and kidneys that politely sigh a little less loudly. The combo pill feels like a mellow jazz riff after a night of heavy metal-smooth, unexpected, and oddly comforting. Some folks swear it whispers calm to the immune army, while others think it just messes with the mood. Either way, it’s a reminder that drugs aren’t just chemicals; they’re stories we tell our bodies, and sometimes the plot twist is a softer inflammation.
Totally agree with the pathway breakdown, Kevin. It’s cool to see how the beta‑blockade and diuretic effects can intersect at the cellular level, especially when you consider the downstream impact on leukocyte adhesion molecules. For patients juggling multiple comorbidities, that kind of nuanced modulation could be a real game‑changer. Keep the jargon coming-it helps us piece the puzzle together.
It is essential, therefore, to underscore that the literature consistently reports a statistically significant decrease in C‑reactive protein levels when patients are administered atenolol‑chlorthalidone; moreover, the adverse event profile remains comparable to monotherapy, provided that electrolyte monitoring is rigorously maintained. Consequently, clinicians should, in my opinion, integrate this combination into therapeutic algorithms with caution, yet confidence.
Definately not every study backs that claim, and alot of the data is from small cohorts, so the whole immuno system effect might be overrated. I think we need bigger trials before we start praising it so much.
Look, the hype around immunomodulation is nothing more than a marketing ploy; the primary function remains blood pressure control, and any peripheral immune effects are incidental at best.
While I respect your scepticism, Patrick, it is prudent to acknowledge that the cardiovascular and immune systems are intricately linked, and even incidental effects can bear clinical significance, especially in long‑term management.
Interesting take on β‑blockers.
The more I think about it, the more it feels like we’re just swapping one set of side‑effects for another, and the supposed immune benefit is a vague afterthought that nobody can quantify.
The article presents a balanced overview, yet it glosses over the potential for electrolyte disturbances to subtly impair innate immune function, particularly neutrophil chemotaxis, which deserves closer scrutiny.
Good point, Claire. Electrolyte shifts can indeed affect neutrophil activity, and clinicians should monitor potassium and magnesium levels to avoid compromising host defenses while using this combo.
It’s reassuring to see that, despite the complexities, the overall safety profile remains favorable when patients adhere to regular check‑ups and maintain a healthy lifestyle alongside medication.
Honestly, the evidence is mixed; some trials show a modest drop in inflammatory markers, while others find no meaningful change, which suggests that any immune benefit may be patient‑specific rather than universal.
Such ambiguity only proves that the pharmaceutical industry loves to sprinkle vague statistics over their brochures, leaving doctors to decipher whether the signal is real or just noise.
When considering the immunological implications, it is worthwhile to remember that lifestyle interventions-regular aerobic exercise, adequate sleep, and a diet rich in antioxidants-can synergize with atenolol‑chlorthalidone to promote a more balanced cytokine milieu.
Wow, this is sooo helpful! Your advice is like a breath of fresh air in the middle of all this med‑talk. I totally get that combining pills with good habits is the way to go. Thanks for the clear, concise rundown.
The discussion gets lost in jargon, but at its core, the combo may simply dampen the overactive immune response that contributes to chronic inflammation, which is a key driver of cardiovascular risk.
One of the most practical considerations when prescribing atenolol‑chlorthalidone is the need for a comprehensive baseline assessment, including complete blood count, renal function, and electrolyte panels, to ensure that any subtle immunological shifts can be tracked over time. In patients with a history of recurrent infections, clinicians might observe a modest reduction in white blood cell variability after initiating therapy, which could reflect the drug’s anti‑inflammatory properties. However, this effect is typically transient and does not usually translate into clinically significant immunosuppression. It is also important to recognize that beta‑blockers have been shown in some studies to modulate T‑cell differentiation, favoring a Th2 response over a Th1 profile, thereby potentially influencing autoimmune disease activity. The thiazide component, on the other hand, can alter calcium handling, which may indirectly affect neutrophil chemotaxis and phagocytic capacity. While these mechanisms are biologically plausible, the magnitude of change observed in routine practice is generally modest. Patients who maintain optimal hydration and dietary potassium are less likely to experience adverse electrolyte shifts that could impair immune function. Regular monitoring, especially in the first three months of therapy, allows providers to adjust dosages before any detrimental effects become entrenched. Moreover, integrating lifestyle interventions such as low‑salt diets and regular moderate‑intensity exercise can amplify the anti‑inflammatory benefits of the medication. For individuals with pre‑existing autoimmune conditions, a careful risk‑benefit analysis should be performed, as the immunomodulatory effects might either ameliorate or exacerbate disease activity depending on the underlying pathology. In the end, shared decision‑making remains paramount; patients should be informed about the potential, albeit limited, impact on their immune system. The overall consensus among cardiologists and immunologists is that the cardiovascular advantages of blood pressure control outweigh the minor immunological concerns. Nonetheless, ongoing research is needed to delineate the long‑term implications of chronic beta‑blocker and diuretic use on immune surveillance. Until more definitive data emerge, clinicians are encouraged to remain vigilant, document any unusual infections, and adjust therapy as clinically indicated. By adopting a proactive and individualized approach, the therapeutic benefits of atenolol‑chlorthalidone can be maximized while minimizing any unintended immune consequences.
Thank you for the thorough overview, Jessica; your detailed guidance on monitoring and lifestyle integration provides a clear roadmap for safely managing both cardiovascular and immune health.