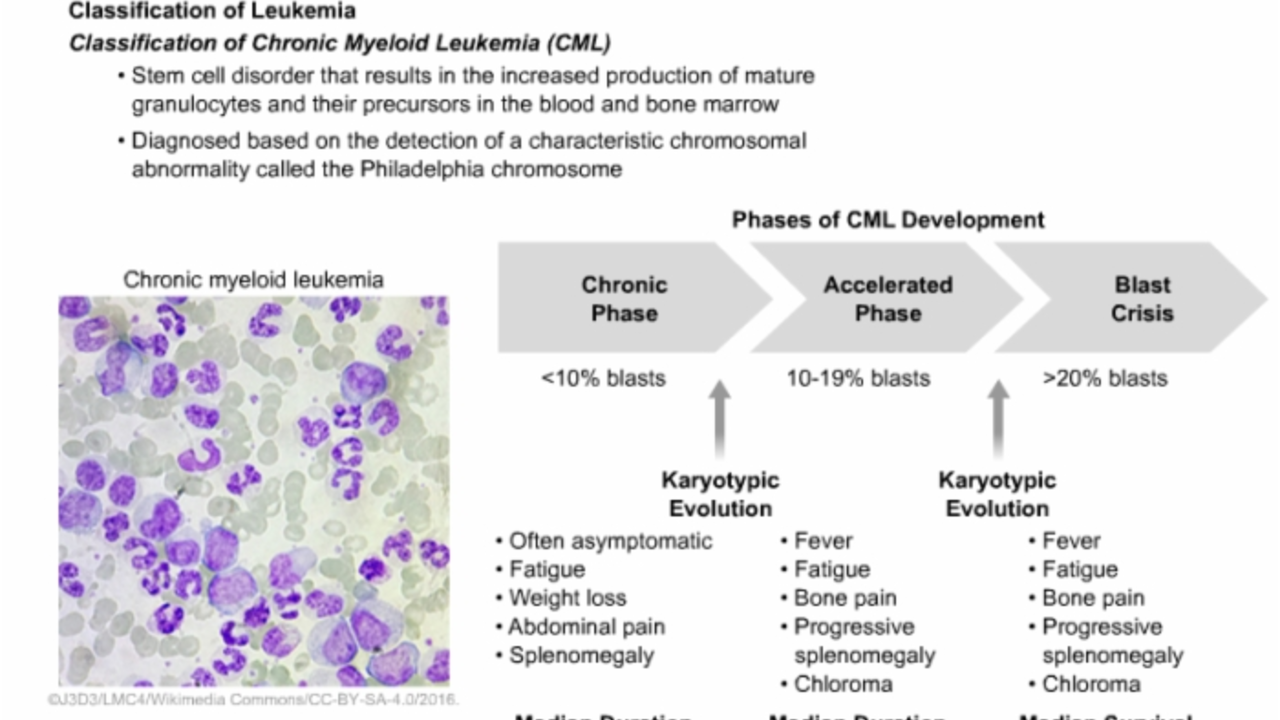
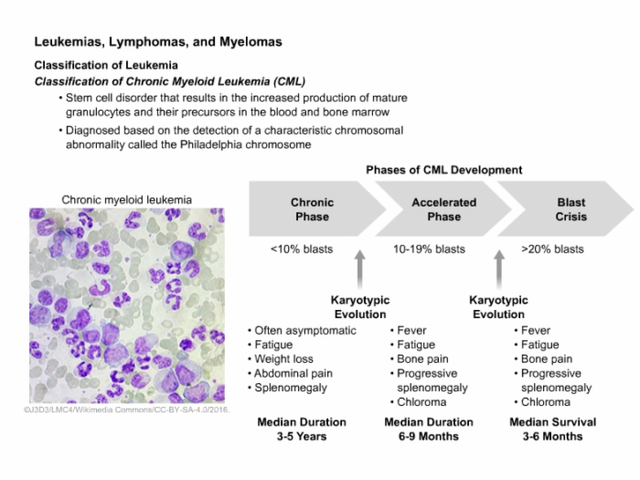
Understanding Chromosome-Positive Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Before we delve into the specific impacts of chromosome-positive lymphoblastic leukemia on fertility and pregnancy, it is crucial to understand what this disease entails. Lymphoblastic leukemia is a type of cancer that begins in the bone marrow and spills over into the blood. The term 'chromosome-positive' refers to the presence of certain genetic markers in the cancerous cells. These markers affect the behavior of the disease and may influence its impact on the patient's fertility and capacity to carry a pregnancy to term.
The Direct Impact of Leukemia on Fertility
Leukemia and its treatments can have a direct impact on fertility. Chemotherapy and radiation therapies, commonly used for treating leukemia, are known to cause fertility issues. These therapies can damage the ovaries or testicles, leading to reduced fertility. Moreover, some medications used to manage leukemia can also affect fertility, either temporarily or permanently. The extent of the impact often varies depending on the age, sex, type of treatment, and individual health conditions of the patient.
Effects of Chromosome-Positive Lymphoblastic Leukemia on Female Fertility
In women, chromosome-positive lymphoblastic leukemia and its treatments can lead to problems like premature ovarian failure, where the ovaries stop functioning before the age of 40. This can lead to infertility and a range of other health issues like osteoporosis. Some women may also experience irregular menstrual cycles or a complete cessation of periods, which can also affect their fertility.
Effects of Chromosome-Positive Lymphoblastic Leukemia on Male Fertility
In men, treatments for chromosome-positive lymphoblastic leukemia can affect sperm production, leading to low sperm count or even infertility. Some men may also experience erectile dysfunction or reduced sexual desire as a side effect of their treatment. The severity and duration of these effects can vary widely between individuals.
Leukemia, Pregnancy, and Potential Risks
Pregnancy is a complex process that can be affected by many factors, including health conditions like leukemia. Women with leukemia may face a higher risk of complications during pregnancy, including miscarriage, preterm labor, and low birth weight babies. There is also a higher risk of maternal mortality. Therefore, it is crucial for women with leukemia to discuss their pregnancy plans with their healthcare team and receive appropriate preconception counseling and care.
The Impact of Leukemia Treatments on Pregnancy
Leukemia treatments can also pose risks to pregnancy. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can harm the developing fetus, especially if administered during the first trimester. Some medications used to treat leukemia can also cross the placenta and affect the fetus. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully plan and manage any necessary treatment during pregnancy.
Preserving Fertility Before Leukemia Treatment
For individuals diagnosed with chromosome-positive lymphoblastic leukemia, who wish to preserve their fertility, several options are available. These include sperm or egg freezing, embryo freezing, and ovarian tissue freezing. The best option will depend on factors like the individual's age, their treatment plan, and their personal preferences.
Conceiving After Leukemia Treatment
Conceiving after leukemia treatment can be a complex process that requires careful planning and medical support. It is generally recommended to wait for a certain period after treatment before trying to conceive, to ensure that any potentially harmful treatments have cleared from the body. Some individuals may also need assistance with conception, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Support and Resources for Patients
Living with leukemia and facing fertility issues or pregnancy complications can be challenging. However, numerous resources are available to support patients, including fertility clinics, support groups, and mental health professionals. It is crucial for individuals to reach out for help and take advantage of these resources to navigate their journey.
Conclusion: The Way Forward
While chromosome-positive lymphoblastic leukemia can pose significant challenges to fertility and pregnancy, it is important to remember that each person's journey is unique. With the right information, support, and medical care, individuals can make informed decisions and find the best path forward for them.
Hey folks love this info It’s good to know there are ways to protect fertility before treatment You can talk with your doctor about sperm or egg freezing It’s not too late to plan for the future Keep hopeful and stay informed
Ugh this article drags on like a bad soap opera
It’s clear that men and women face different risks but why aren’t we hearing more about long‑term hormonal impacts 😠 We need better data and support for survivors
Thanks for sharing the details 🙏 If anyone’s looking into fertility preservation options remember clinics can guide you through egg, sperm, or tissue freezing It’s a team effort and you’re not alone
While the exposition admirably canvasses the oncologic‑reproductive interface, it regrettably eschews a granular dissection of epigenetic sequelae inherent to chromosomal translocations. The lexicon oscillates between clinical sobriety and florid hyperbole, thereby obfuscating the quintessential pathophysiological mechanisms. A more rigorous delineation of iatrogenic gonadotoxicity, juxtaposed with a nuanced appraisal of survivorship quality‑of‑life indices, would elevate the discourse to a scholarly echelon.
Life and disease are intertwined in ways that make the mind wander like a restless river.
When a young body battles chromosome‑positive lymphoblastic leukemia, the usual hopes of future parenthood become a distant echo.
The chemo blasts act like a storm, shredding not only the malignant cells but also the delicate garden of germ cells.
Some say that fertility preservation is a safety net, yet it feels more like a gamble with fate.
Egg freezing can be likened to pressing pause on a melody, hoping the music will resume once the chaos subsides.
Sperm banking, on the other hand, is like storing a spark for later ignition, fragile but full of potential.
Doctors often advise waiting a set period after treatment before trying to conceive, which can test a patient’s patience to the brink.
In many cultures this waiting period is seen as a rite of passage, a test of resilience and will.
But the true test is not just the calendar; it is the inner dialogue that whispers, ‘Will my body ever cooperate?’
Modern reproductive tech offers IVF and pre‑implantation genetic testing, tools that were once the stuff of sci‑fi.
Yet these advances come with their own ethical quandaries and financial burdens that can weigh heavily on survivors.
In the philosophy of stoicism, one learns to focus on what is within control – the choice to seek help, the decision to support fellow patients.
Support groups act as a lighthouse, guiding those lost in the fog of uncertainty.
Ultimately, the journey from diagnosis to parenthood is a mosaic of medical science, personal resolve, and societal support.
Embrace the knowledge, lean on the community, and remember that hope, though sometimes flickering, is never truly extinguished.
Listen up – don’t let leukemia dictate your destiny! You have the power to fight, to plan, to secure your future family. Get on board with fertility specialists now, no excuses! This is your battle, own it and smash every obstacle.